Home
Tutorial's
Image collection
Calculator
Projects
MCQ's
3d Models
Invention Hub
How it works
Download Our app
Module 11: Electric Power and Energy
11.1 : Electrical Power
Electric power is defined as the rate at which electrical energy is converted into other forms of energy (e.g., heat, etc.). For example, a fan converts the electric energy into kinetic energy; similarly, a bulb converts the electrical energy into heat and light in t seconds.
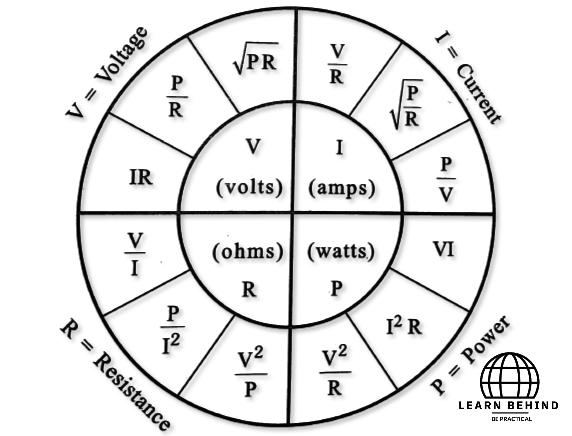
Electric Power = qv/t
=(it)v/t J/s or watts where q=it
= VI watts
=I R
=
From above, any formula you can use for problems depending on the problem
In practical applications, you can calculate the power consumption of devices. For example, if you see any mobile charge label, the output rating is mentioned on the charger, like 5V-2A, which determines that it is a 10W charger.
11.2 : Electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred into other forms when current flows through a circuit due to resistance.

In the above figure, as the charge q=It moves from point A to B, it loses electric potential energy. This loss of electric potential energy is converted into another energy
Electrical energy consumed W= VIt = I2 R t = V2t/R joules.
Power Triangle
Related articles
