Home
Tutorial's
Image collection
Calculator
Projects
MCQ's
3d Models
Invention Hub
How it works
Download Our app
Module 16: Calculations in Parallel Connection
Consider two resistances R1 and R2 are connected in series across a potential difference of V volts as shown in figure.
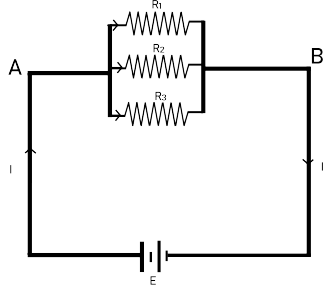
The total current ‘I’ divides into two parts I1 and I2 .I1 flowing through the R1 and I2 flowing through the R2.Then the total resistance of the circuit is,
Req=R1R2/R1+R2
Applied voltage is , V=I*Req
Voltage across resistance R1, V1=I1*R1
Voltage across resistance R2, V2=I2*R2
In parallel circuit the voltage across all the resistances is same therefore,
V = V1 = V2
V=I1*R1
I1 = V/R1 ----(1)
Where V=IReq
=I(R1*R2/R1+R2) from module 14
Substitute in eq (1)
I1 = I(R1*R2/(R1+R2)R2)
I1 = I*R2/R1+R2
Similarly,
I2= I*R1/R1+R2
• Current through one of the resistance = Total current* opposite resistance/sum of the product of all resistances connected in parallel
