Home
Tutorial's
Image collection
Calculator
Projects
MCQ's
3d Models
Invention Hub
How it works
Download Our app
(Last updated on 12-09-2024)
Module 20: Joules Law of electric heating
Joules law describes the relationship between the heat produced in a conductor and the electric current flow through it.
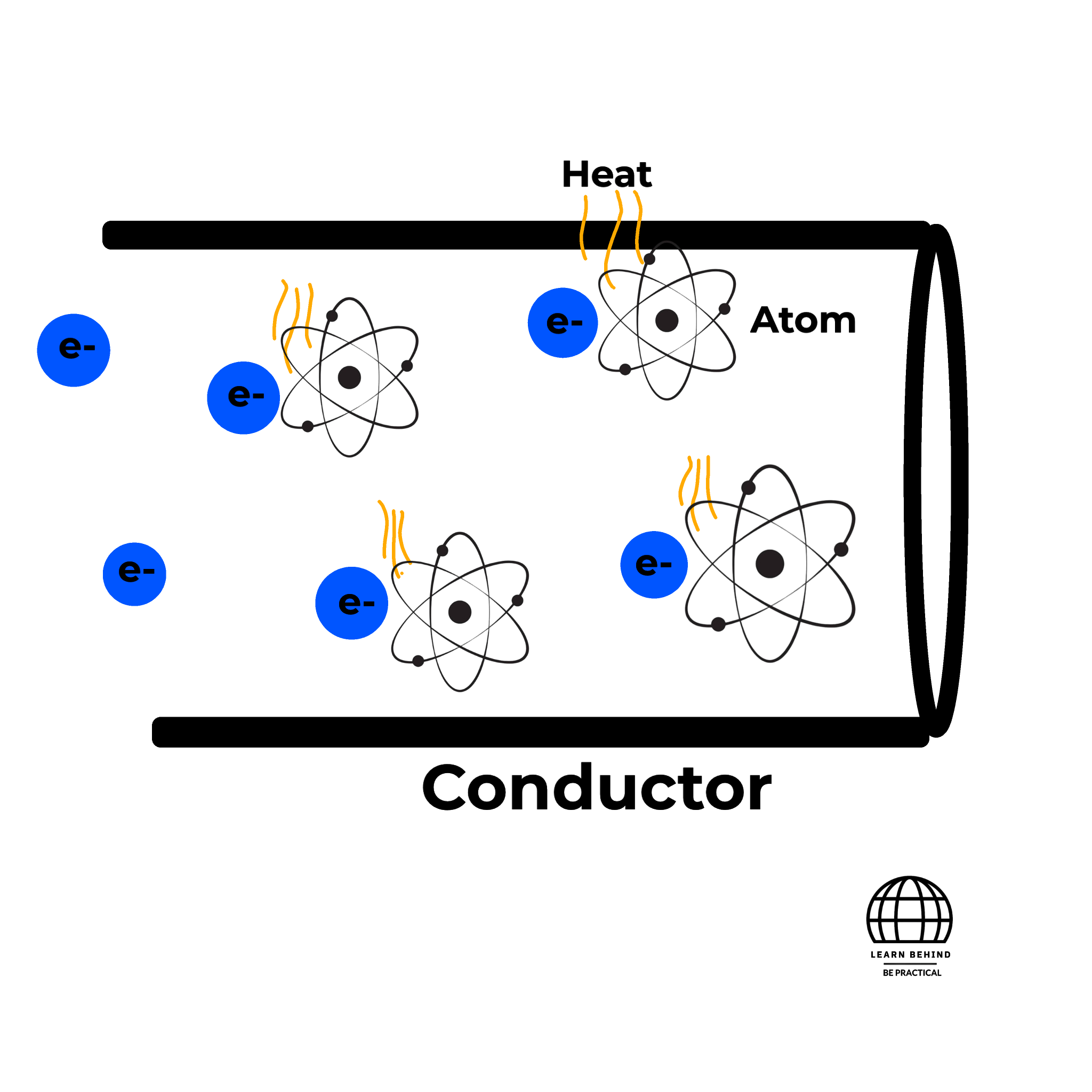
When an electric current flows through a conductor, the electrons collide with the atoms of the conductor. These collisions result in the conversion of electric energy into heat energy. The more electrons flow, more collisions occur, leading to more heat generation.
According to Joules law the heat produced ‘H’ is directly proportional to the :
(i) Square of the current passing through the conductor, I2
(ii) Resistance of the conductor, R
(ii) (iii) Time for which current passes through the conductor, t
Therefore,
Heat Produced, H ∝ I2 R t Joules
(or) H = I2 R t/J
Where J is the constant and is known as the mechanical equivalent of heat. It’s value is 4.185 (4.2) joule/calorie or 4200 joule/kilo calorie
Heat Produced , H = I2 R T/4.2 calorie
= I2 R T/4200 Kilo calorie
Thermal Efficiency:
The ratio of heat actually used to the total amount of heat produced electrically is known as thermal efficiency.
. It is denoted by the letter Th and expressed in percentages (%).
Th = Heat actually utilized/Total heat produced electrically.
Related articles
